Education
Education and early development of the brain is highly influenced by exposure to the world and many of the things it has to offer. Children that have been stimulated with positive experiences often have a much larger brain size and capacity then those that are neglected or grow up with crime and violence.
Standardized Testing
- EQAO Provincial Standard Tests
- % At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 3 EQAO Testing
- % At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 6 EQAO Testing
- % At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 9 EQAO Testing
- % Successful on the Ontario Secondary School Literacy Test (OSSLT)
EQAO Testing
The Education Quality and Accountability Office (EQAO) was established to gather information from—and account for—every student in the public education system. Ontario’s province-wide tests assess cumulative knowledge and skills at four key stages:
- Grade 3 (literacy and math tested at the end of the primary division);
- Grade 6 (literacy and math tested at the end of the junior division);
- Grade 9 (math tested in the first year of secondary school) and
- Grade 10 (literacy tested as a graduation requirement [i]
Student achievement results have always been considered key indicators of educational quality, and student scores on large-scale assessments are the subject of public interest. However, test scores can be interpreted meaningfully only in the context of the system that produced them. Understanding and evaluating the quality of education requires not just numerical values or quantitative result measures such as achievement, but a more comprehensive picture of the unique and complex characteristics of students, schools, boards and the province. Information about local student achievement has proven essential for effective system-improvement planning. The assessments provide individual student, school, school board and province-wide results on student achievement of selected Ontario Curriculum expectations. [ii]
Other Sources Reviewed Throughout the Formation of this Report
Brooks-Gunn, J., Denner, J., & Klebanov, P.K. (1995). Families and neighborhoods as contexts for the education. In E. &. Passow (Ed.), Changing populations changing schools: Ninety-fourth Yearbook of the National Society for the Study of Education, Part II (pp. 233-252). Chicago: The National Society for the Study of Education.
Early Math Strategy Expert Panel in Ontario. (2003). Early Math Strategy. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/math/math.pdf
Education Quality and Accountability Office (EQAO). (2012). EQAO’s Provincial Elementary School Report: Results of the 2011-2012 Assessments of Reading, Writing and Mathematics, Primary Division (grades 1 – 3) and Junior Division (grades 4 – 6). Toronto: EQAO. Retrieved from http://www.eqao.com/ProvincialReport/ProvincialReport.aspx?Lang=E&yr=12&cat=e
Emenogu, B. (undated). Strong Writing Skills May Enhance Students’ Chances for Success. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/literacynumeracy/inspire/classroom/strongSkills.html
EQAO. (2012a). The Power of Ontario’s Provincial Testing Program. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
EQAO. (2012b). EQAO’s Technical Report for the 2010-2011 Assessments. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario. Retrieved from http://www.eqao.com/pdf_e/12/2011_TechnicalReport_en.pdf
Expert Panel on Early Reading in Ontario. (2003). The Report of the Expert Panel on Early Reading in Ontario, 2003. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/reading/reading.pdf
Expert Panel on Literacy in Grades 4 to 6. (2004). Literacy for Learning. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/literacy/panel/literacy.pdf
Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 in Ontario. (2004). eaching and Learning Mathematics: The Report of the Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 Ontario. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/numeracy/panel/numeracy.pdf
Expert Panel on Student Success in Ontario: Mathematical Literacy, Grades 7–12. (2004). Leading Math Success: Mathematical Literacy, Grades 7 – 12. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/numeracy/numeracyreport.pdf
Expert Panel on Students at Risk in Ontario. (2003). Think Literacy Success Grades 7 – 12: Report of the Expert Panel on Students at Risk in Ontario. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/literacyreport.pdf
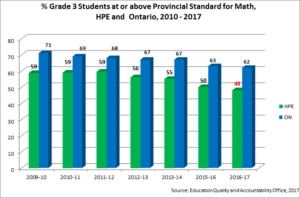
% At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 3 EQAO Math
What does this measure?
The mathematics component of EQAO assesses students on their knowledge and skill across the five mathematical strands in the curriculum: number sense and numeration, measurement, geometry and spatial sense, patterning and algebra, and data management and probability. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.[iii]
Why is this important?
It is critical that mathematical skills, an understanding of key concepts and a positive attitude about mathematics are developed in the early grades.[iv] Mathematics helps students acquire a framework for:
- reasoning
- justifying conclusions, and
- expressing ideas clearly.
A solid understanding of mathematical concepts is important in our information- and technology-based society. [v]
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The proportion of grade 3 students who meet the provincial standard in HPE is consistently at least 10% lower than the provincial average. Despite the Ministry of Education goal of 75% of children at or above the provincial standard, fewer than 60% of grade 3 students in HPE meet or exceed that standard. There has been no significant change in the last 5 years in the Grade 3 mathematics success of HPE students.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE.
[i] EQAO. (2012a). The Power of Ontario’s Provincial Testing Program. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
[ii] EQAO. (2012a). The Power of Ontario’s Provincial Testing Program. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
[iii] EQAO. (2012b). EQAO’s Technical Report for the 2010-2011 Assessments. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario. Retrieved from http://www.eqao.com/pdf_e/12/2011_TechnicalReport_en.pdf
[iv] Early Math Strategy Expert Panel in Ontario. (2003). Early Math Strategy. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/math/math.pdf
[v] Ontario Ministry of Education. (2005). The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 1 to 8: Mathematics, 2005. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/curriculum/elementary/math18curr.pdf
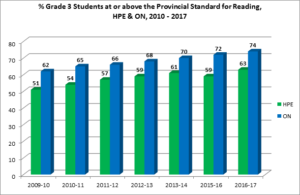
% At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 3 EQAO Reading
What does this measure?
The reading component assesses students on their skill at understanding explicit and implicit information and ideas in a variety of text types required by the curriculum. The reading component also requires students to make connections between what they read and their own personal knowledge and experience. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
Reading success is the foundation for achievement throughout the school years and beyond. Children must be taught to understand and interpret printed language. There is a critical window of opportunity from the ages of four to seven for learning to read. Children who struggle with reading in the primary grades (1 to 3) are at a serious disadvantage. Academically, they have a much harder time keeping up with their peers, and they increasingly fall behind in other subjects. They are far more likely to suffer low self-esteem and, in their teen years, are more likely to drop out without completing high school[i] .
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The proportion of grade 3 students who meet the provincial standard in HPE is consistently lower than the provincial average. However, there has been a substantial improvement in the last five years, even though the gap between the students in HPE and those in Ontario is closing slightly. Despite the Ministry of Education goal of 75% of children at or above the provincial standard, just over 60% of grade 3 students in HPE now meet or exceed that standard.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE.
[i] Expert Panel on Early Reading in Ontario. (2003). The Report of the Expert Panel on Early Reading in Ontario, 2003. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/reading/reading.pdf
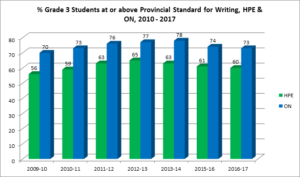
% At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 3 EQAO Writing
What does this measure?
The writing component assesses students on their skill at organizing main ideas and supporting details using correct spelling, grammar and punctuation in a variety of written communication forms required by the curriculum. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
Writing skills are important for communicating. Writing allows students to:
- “connect the dots” in their knowledge
- express themselves
- participate in society
- achieve educational and career success[i].
Getting elementary students to start to write early has a strong positive impact on the way they think, the amount they read, and their achievement later in life[ii].
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The proportion of grade 3 students who meet the provincial standard in HPE had been consistently increasing, but in 2014, it decreased slightly, and remains more than 10% lower than the provincial average and the Ministry of Education goal of 75% of children at or above the provincial standard. However, in the last 5 years, the success rate of students in HPE has moved from slightly over half to close to two-thirds meeting the standard.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE
[i] National Commission on Writing in America’s Families, Schools, and Colleges. (2003). The Neglected “R”: The Need for a Writing Revolution. Avaioable at: http://www.collegeboard.com/prod_downloads/writingcom/neglectedr.pdf
[ii] Emenogu, B. (undated). Strong Writing Skills May Enhance Students’ Chances for Success. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/literacynumeracy/inspire/classroom/strongSkills.html
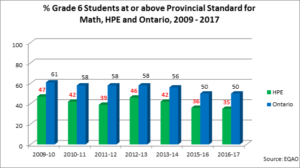
% At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 6 EQAO Math
What does this measure?
The mathematics component assesses students on their knowledge and skill across the five mathematical strands in the curriculum: number sense and numeration, measurement, geometry and spatial sense, patterning and algebra, and data management and probability. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement in reading, writing and mathematics. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
The junior years are an important time of transition and growth in students’ mathematical thinking. In Grades 4–6, the mathematics curriculum is changing in its content, sophistication, abstraction, and expectations of student proficiency. There is also a move to more abstract reasoning and complex ideas in the junior grades. Junior students begin to solve problems in more than one way and develop their ability to communicate their thinking to others orally and on paper. [i]
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
Hastings Prince Edward has not seen an improvement in mathematical understanding among many students. For more than half of the HPE students, mathematics remains a subject that they learn to fear and dislike as they move through the grades. Rather than developing mathematical literacy and confidence in their ability to do math, some students become less confident mathematically, learn to stop thinking mathematically, and come to rely on memorizing procedures to get correct answers[ii]. Since 2009/10, fewer than half of grade 6 students in HPE meet the provincial standard, well below the provincial average.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE.
[i] Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 in Ontario. (2004). eaching and Learning Mathematics: The Report of the Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 Ontario. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/numeracy/panel/numeracy.pdf
[ii] Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 in Ontario. (2004). eaching and Learning Mathematics: The Report of the Expert Panel on Mathematics in Grades 4 to 6 Ontario. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/numeracy/panel/numeracy.pdf
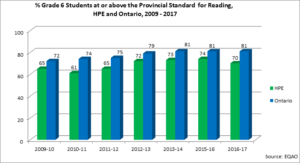
% AT OR ABOVE THE PROVINCIAL STANDARD GRADE 6 EQAO Reading
What does this measure?
The reading component assesses students on their skill at understanding explicit and implicit information and ideas in a variety of text types required by the curriculum. The reading component also requires students to make connections between what they read and their own personal knowledge and experience. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
Literacy, including reading, is an important path to learning and can change children’s lives. Junior students can:
- learn to engage with new ideas as they read, write, and talk about a broad range of topics and experiences
- acquire insight into their own thought
- connect to the texts they read and write.
With the diversity and increasing complexity of texts in the junior grades, it becomes important for students to move beyond literal comprehension and to think critically. Critical-literacy skills equip students with knowledge, skills, and confidence to develop their own perspectives and worldview[i] (Expert Panel on Literacy in Grades 4 to 6, 2004).
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The reading scores for Grade 6 students in HPE have been increasing gradually over the last 5 years, until 2017. While the scores are still slightly below the provincial average, the gap is smaller than for other EQAO tests at the primary and junior levels.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE.
[i] Expert Panel on Literacy in Grades 4 to 6. (2004). Literacy for Learning. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/literacy/panel/literacy.pdf
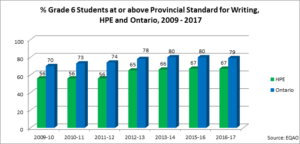
% At or Above the Provincial Standard Grade 6 EQAO Writing
What does this measure?
The writing component assesses students on their skill at organizing main ideas and supporting details using correct spelling, grammar and punctuation in a variety of written communication forms required by the curriculum. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
In the junior grades, writing provides students with opportunities to learn about themselves and their connections to the world. Through writing, students:
- organize their thoughts
- remember important information
- solve problems
- understand their own thoughts and feelings and the events in their lives
- reflect on a widening range of perspectives, and
- learn how to communicate effectively for specific purposes and audiences.
By putting their thoughts into words and supporting the words with visual images in a range of media, students acquire knowledge and deepen their understanding of the content in all school subjects. Writing also helps students to better.[i]
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The proportion of grade 6 students who meet the provincial standard in HPE is increasing, particularly in the 2012/13 school year, going from just over 50% five years ago to 2/3. Nevertheless, HPE students remain more than 10% lower than the Ontario average.
Notes about the data
Schools in the ALCDSB with fewer than 10 participants were excluded from the calculations for HPE.
[i] Expert Panel on Literacy in Grades 4 to 6. (2004). Literacy for Learning. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/literacy/panel/literacy.pdf
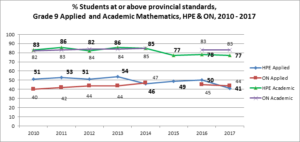
% AT OR ABOVE THE PROVINCIAL STANDARD GRADE 9 EQAO Mathematics
What does this measure?
The Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics measures how well students have met the expectations outlined in The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 9 and 10: Mathematics. EQAO develops separate versions of the Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics for students in academic and applied courses. Students in Grade 9 academic mathematics are assessed on their knowledge and skill across the four mathematical strands in the curriculum: number sense and algebra, linear relations, analytic geometry, and measurement and geometry. Students in Grade 9 applied mathematics are assessed on their knowledge and skill across the three mathematical strands in the curriculum: number sense and algebra, linear relations, and measurement and geometry. The four achievement levels defined in The Ontario Curriculum are used by EQAO to report on student achievement. Level 3 has been established as the provincial standard. Levels 1 and 2 indicate achievement below the provincial standard, and Level 4 indicates achievement above the provincial standard.
Why is this important?
Mathematics empowers individuals to describe, analyse, and understand the world we live in. [i] The Expert Panel looking at mathematical literacy in grades 7 – 12 concluded:
Mathematical literacy is as important as proficiency in reading and writing. Mathematics is so entwined with today’s way of life that we cannot fully comprehend the information that surrounds us without a basic understanding of mathematical ideas. Confidence and competence in mathematics lead to productive participation in today’s complex information society and open the door to opportunity. (p.10)
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
On the Applied Mathematics test, HPE grade 9 students have consistently scored above Ontario students, although in 2014 and 2016, they slipped below the Ontario average. On the academic test, HPE students’ results are more or less at the provincial average , although in the last few years, they have slipped below 80% who meet provincial standards
Graphs
[i] Expert Panel on Student Success in Ontario: Mathematical Literacy, Grades 7–12. (2004). Leading Math Success: Mathematical Literacy, Grades 7 – 12. Toronto: Ministry of Education. Retrieved from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/reports/numeracy/numeracyreport.pdf
What does this measure?
The OSSLT assesses Grade 10 students’ literacy skills based on reading and writing curriculum expectations across all subjects in The Ontario Curriculum up to the end of Grade 9. The reading component assesses students’ skills at understanding explicit and implicit information and ideas in a variety of text types required by the curriculum. It also assesses their ability to make connections between what they read and their own personal knowledge and experience. The writing component assesses students’ skill at organizing main ideas and supporting details using correct spelling, grammar and punctuation for communication in written forms. For the OSSLT, EQAO reports only two levels of achievement: successful and unsuccessful. Students must achieve a minimum score to receive a successful result on the OSSLT.
Why is this important?
The single most important purpose of education is to equip all students with the literacy and numeracy skills for lifelong learning. Literacy combines skills and knowledge in:
- reading
- writing
- speaking and
- listening
Literacy becomes the ability to understand, think, apply, and communicate effectively to achieve personal and career goals and to solve increasingly complex problems and make decisions in a richly diverse, information-driven society . (Expert Panel on Students at Risk in Ontario, 2003, p. 12)
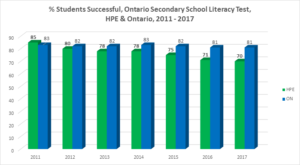
How is Hastings Prince Edward area doing?
The vast majority of HPE grade 10 students are successful on the OSSLT. Nevertheless, there has been a downward trend and an increasing gap in the last few years between HPE and Ontario results.
Graphs